To ensure accurate and precise operation of Analytics algorithms, it is important to account for the unique parameters of every implementation scenario. A correctly selected and properly installed video camera is essential for acquiring high-quality data, which underpins the reliable and efficient performance of a video analytics system. Parameters such as the camera’s tilt angle, mounting height, focal length, and scene illumination directly influence the quality of the video stream received from the camera and, consequently, the accuracy of video analytics algorithms.
On this page, you find the guidelines for the following Analytics types:
-
People counting in an area
-
Visitor counting
-
Line crossing detection
The present guideline defines the overall requirements, including:
Video camera specifications
|
Specifications |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Matrix It is a key component of a camera that defines image quality. The value of this component reflects the size of the matrix diagonal in inches. |
1/3 inches and larger, with a high degree of sensitivity to light. |
|
Lens-aperture ratio (light sensitivity) Plays a crucial role in overall image quality. Lens aperture is the maximum light capacity of a lens, which determines how much light can pass through to the camera sensor. The F-number means the maximum size of the aperture. The smaller the F-number, the more light the lens can gather. |
F1.4 and better |
|
Lens aperture With this camera component, you can set the amount of light that goes through the lens and control the focus depth. Located within the lens itself, the aperture regulates light intake by altering the size of the opening. |
With adjustable settings (it’s important to be able to set the limits of the lens aperture opening and closing). |
Camera placement requirements
Distance and mounting height parameters
Set the mounting height and the distance to the objects separately for each camera. These parameters depend on the image quality at the periphery of the monitored zones and the required viewing angles for the chosen Analytics type.
Angles and orientation
It is recommended to install the camera vertically, as other installation methods may negatively affect the accuracy of Analytics.
The angle between the optical axis of the lens and the horizontal line should not exceed 45°.
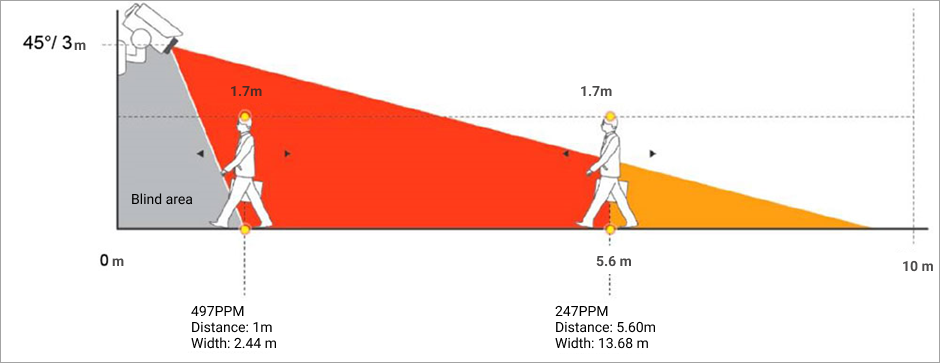
Example
If a camera with a vision angle of 45° is mounted at a height of 3 meters, the blind zone is equal to 1 meter from the camera projection onto the horizontal surface plane in the case of detecting a person who is 170 cm tall. See the image below.
The width of the area immediately before the blind zone, where a person is visible, is 2.5 meters. At a distance of 5.5 meters, a person will be visible to two-thirds of their height (only the lower part of the body). At this point, the camera’s field of view is approximately 13.5 meters.
Camera mobility
The camera must remain stationary.
Illumination
Illumination should be 150 lux or higher. The lighting conditions within the camera control area should be ample and uniform, excluding any side light sources. For example, to control the entrance group, prevent the camera from being illuminated by streetlights.
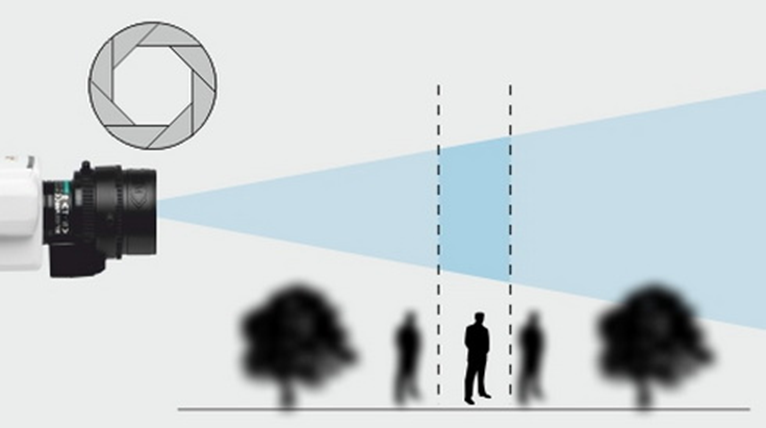
The depth of field
Camera depth of field should cover an entire control zone. The greater the depth of field, the larger part of the frame will be clear. The depth of field depends on the focal lens and the value of the lens aperture ratio. We recommend calculating the camera depth of field in advance (which is particularly relevant for long-focus lenses) and getting a camera with adjustable lens aperture settings (including the possibility to set the lens aperture opening and closing limits).

Camera field of view and object counting
To ensure accurate Analytics performance, a camera with relevant specifications should be placed according to the requirements, as well as the following requirements should be met:
-
Image orientation: objects must be positioned right side up. If the camera image is inverted (or upside down), it must be flipped vertically or horizontally using the camera menu.
.png?cb=d29843ff188e3bf93ee45338456bf691)
-
The speed of objects shouldn’t be higher than 0.5–1.5 m/sec to avoid counting inefficiency.
-
Objects should be visible at full height and shouldn’t overlap each other.
-
An image should be clear and sharp.
-
Illumination should be uniform.
-
Background should be neutral.
-
Avoid foreign moving objects in the detection area for People counting in an area.
-
There is no limit to the number of objects simultaneously crossing the line (relevant for Visitors counting and Line crossing detection). Missed detections are possible because of the high density of objects (see the image below).